The Complete Website Guide – Website Types, Tools, SEO, and Maintenance
Learn why a website still matters in 2025 and how to build one step-by-step. Explore website types (blogs, e‑commerce, corporate, portfolios), required resources (domain, hosting, CMS, design), SEO best practices, costs, and maintenance
The Importance of Websites for Individuals and Businesses: A Complete Guide
- This guide explains in plain English why a website is essential, the types of websites you can build, the resources you need (domain, hosting, CMS, design tools), and a step‑by‑step build process with SEO best practices.
- You’ll also find cost estimates, a maintenance checklist, common mistakes to avoid, and tool recommendations—aligned with Google’s EEAT principles for credibility and clarity.
Why a website still matters in 2025
- Your website is the one digital asset you fully own. Social platforms change, algorithms shift—your site remains your home base.
- It works 24/7: builds credibility, attracts leads, sells products, and supports customers.
- It’s measurable and scalable: analytics reveal what works so you can improve.
Benefits for individuals
- Credibility: a professional online presence beats a resume alone.
- Opportunity: showcase skills and portfolio; attract clients and employers.
- Control: choose your design, content, and brand voice.
Benefits for businesses
- Discovery: rank for buyer-intent keywords, capture local searches.
- Conversions: convert traffic into leads and sales with landing pages and CTAs.
- Support and retention: FAQs, help centers, and resources reduce churn.
Types of websites (with goals, pages, platforms)

Personal blog and content site
- Primary goals: build audience, newsletter signups, affiliate revenue.
- Core pages: Home, About, Blog, Categories/Tags, Contact.
- Good platforms: WordPress, Squarespace, Ghost.
- Success metrics: organic traffic, email subscribers, time on page.
Portfolio website (creatives, freelancers, agencies)
- Primary goals: showcase work, win clients, establish authority.
- Core pages: Work/Case Studies, Services, About, Testimonials, Contact.
- Good platforms: Webflow, WordPress + builder, Squarespace.
- Success metrics: inquiries, booked calls, proposal requests.
E‑commerce website (online store)
- Primary goals: sales, AOV, repeat purchases, subscriptions.
- Core pages: Home, Category, Product, Cart/Checkout, Policies.
- Good platforms: Shopify, WooCommerce (WordPress), BigCommerce.
- Success metrics: conversion rate, revenue, returning customer rate.
Corporate/SMB website (services and B2B)
- Primary goals: leads (demos, quotes), trust signals, support.
- Core pages: Services, Industries, Case Studies, About/Team, Resources, Contact.
- Good platforms: WordPress, Webflow, HubSpot CMS.
- Success metrics: qualified leads, demo requests, pipeline value.
Informational portal/resource hub
- Primary goals: traffic growth, ad revenue, community trust.
- Core pages: Topics, Guides, Tools/Calculators, Newsletter, About.
- Good platforms: WordPress, Headless CMS (Contentful/Sanity).
- Success metrics: sessions, pages per session, subscriber growth.
Online course (LMS) and membership site
- Primary goals: course sales, member retention, recurring revenue.
- Core pages: Curriculum, Lessons, Pricing, Account, Community.
- Good platforms: Teachable/Thinkific, WordPress + LearnDash, Kajabi.
- Success metrics: enrollments, completion rate, MRR/churn.
Community forum and knowledge base
- Primary goals: peer support, engagement, UGC.
- Core pages: Categories, Threads, Search, Guidelines, Help.
- Good platforms: Discourse, Tribe, WordPress + bbPress.
- Success metrics: active users, posts, solution rate.
Nonprofit/charity website
- Primary goals: donations, volunteers, program impact.
- Core pages: Mission, Programs, Donate, Events, Reports, Contact.
- Good platforms: WordPress, NationBuilder.
- Success metrics: donation volume, volunteer signups, grant credibility.
Product landing page and microsite
- Primary goals: validate ideas, collect signups, preorders.
- Core sections: Hero + value prop, benefits, social proof, CTA, FAQ.
- Good platforms: Webflow, Framer, WordPress + builder.
- Success metrics: conversion rate, waitlist growth, CAC tests.
What you need to build a website (resources)

Identity: domain, DNS, SSL/TLS
- Domain registration: short, memorable, brandable; enable auto‑renew.
- DNS hosting: use a reliable provider; keep records organized (A, CNAME, MX).
- SSL/TLS: always-on HTTPS for security and SEO trust.
Best practices
- Prefer .com or relevant ccTLD; protect key variations.
- Use DNS and registrar with 2FA and role‑based access.
Infrastructure: web hosting, CDN, backups
- Hosting options: shared (starter), VPS (scalable), managed WordPress, or cloud (AWS/GCP/Azure).
- CDN: speed up global delivery; reduce origin load.
- Backups: automated daily + on‑demand; test restores; keep offsite copies.
Best practices
- Choose hosting matched to traffic and stack; monitor uptime and performance.
Platform: CMS and essential extensions
- CMS choices: WordPress (flexible), Shopify (e‑commerce), Webflow (visual design), Wix/Squarespace (no‑code).
- Themes/templates: start with clean, fast, accessible designs.
- Plugins/apps: forms, SEO, caching, security, schema, analytics.
Best practices
- Keep the stack lean; only install well‑maintained, reputable extensions.
Design: UX, brand kit, accessibility
- Wireframes and mockups: map layouts before building.
- Brand kit: logo, colors, typography; ensure color contrast.
- Responsive/mobile‑first: test across devices; optimize navigation and CTAs.
Best practices
- Add alt text, focus states, and keyboard navigation (WCAG guidelines).
Content: copy, media, legal pages
- Copywriting: clear benefits, scannable headings, strong CTAs.
- Media: authentic images, short videos, compressed and lazy‑loaded.
- Legal: privacy policy, terms, cookie policy; shipping/returns for stores.
Best practices
- Use a content calendar; refresh and repurpose high‑value posts.
Marketing: SEO, analytics, email
- SEO: keyword research, on‑page optimization, internal linking.
- Analytics: GA4, Search Console; set up goals/events and dashboards.
- Email: lead magnets, welcome series, segmentation, deliverability.
Best practices
- Track campaigns with UTM; measure assisted conversions, not just last click.
Security & compliance
- Updates: core, themes, plugins; test in staging first.
- Firewall/WAF and malware scanning; limit login attempts and enable 2FA.
- Compliance: GDPR, cookie consent, accessibility, PCI for e‑commerce.
Best practices
- Maintain a written incident response plan and access control policy.
Operations: maintenance and SOPs
- Maintenance schedule: monthly updates, quarterly audits.
- Monitoring: uptime, Core Web Vitals, error logs, broken links.
- SOPs: clear processes for content, releases, and approvals.
Step‑by‑step: how to build and maintain a website
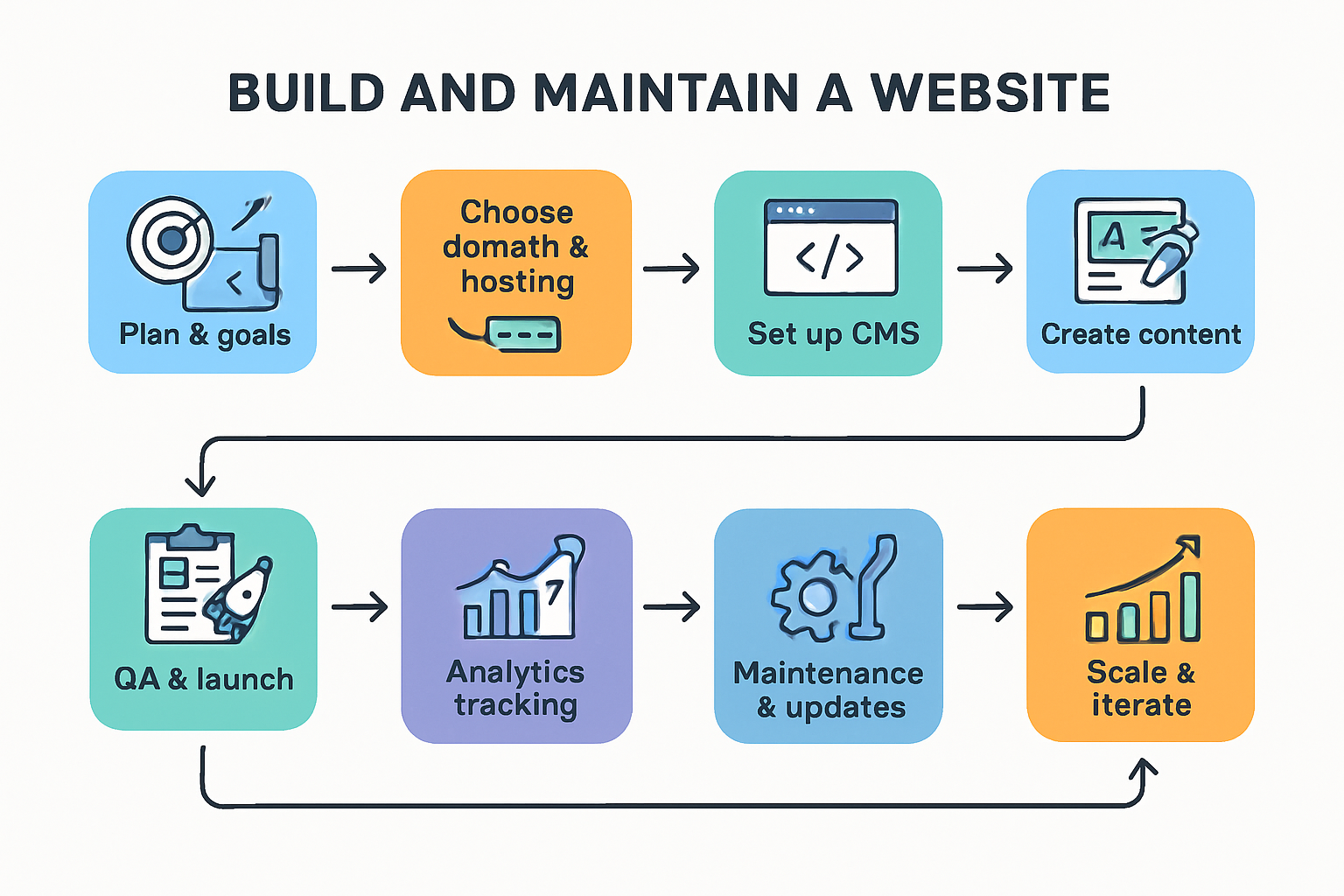
1) Plan: goals, audience, sitemap
- Define ICP, value proposition, and success metrics (leads, sales, signups).
- Draft sitemap and content plan; list required features and integrations.
Deliverables
- Brief, sitemap, wireframes, initial keyword list.
2) Choose domain and hosting
- Register your domain; configure DNS and SSL.
- Select hosting tier (shared, VPS, managed) based on traffic and stack.
Deliverables
- Live domain on HTTPS, DNS records, hosting credentials.
3) Set up your CMS and essentials
- Install CMS/platform; add theme/template and must‑have plugins/apps.
- Configure backups, roles/permissions, and a staging environment.
Deliverables
- Clean, secure base site with version control and backup in place.
4) Design and build (mobile‑first)
- Create reusable components (header, footer, nav, cards).
- Build templates for core pages; ensure accessibility and performance.
Deliverables
- Design system, responsive templates, performance budget.
5) Create content and CTAs
- Write concise, benefit‑driven copy; add images/video with alt text.
- Place clear CTAs on every page; map internal links.
Deliverables
- Final copy and media, approved page drafts, internal linking plan.
6) SEO and performance tuning
- Optimize titles, meta descriptions, headings, schema, and URLs.
- Compress images, enable caching/HTTP/2, minify assets; fix CWV issues.
Deliverables
- On‑page SEO checklist completed; passing Core Web Vitals.
7) QA testing and launch
- Test forms, checkout, search, and navigation on multiple devices/browsers.
- Set 301 redirects, custom 404, sitemap.xml, robots.txt, cookie banner.
Deliverables
- Launch checklist signed off; go‑live plan executed.
8) Analytics and tracking
- Implement GA4, Search Console, pixels, and consent mode.
- Create dashboards for traffic, conversions, and content performance.
Deliverables
- Verified data streams, KPIs dashboard, reporting cadence.
9) Maintenance and continuous improvement
- Update software monthly; review security and performance.
- Ship content regularly; A/B test headlines and CTAs; iterate based on data.
Deliverables
- Maintenance log, content calendar, test-and-learn roadmap.
SEO best practices (simple and effective)
Keyword strategy
- Map one primary keyword per page and 3–5 related terms.
- Examples to use naturally: website design, web hosting, domain registration, content management system, e‑commerce website, SEO optimization, website maintenance, small business website, portfolio website.
Quick checklist
- Search intent match, SERP scan, unique angle, internal link plan.
On‑page optimization
- One H1, descriptive H2/H3/H4; short paragraphs and bullet points.
- Unique title tags (50–60 chars) and meta descriptions (140–160 chars).
- Descriptive alt text, logical internal links, clean URL slugs.
Technical SEO
- Fast loads: image compression, caching, minification, CDN.
- Mobile‑first, secure HTTPS, proper 301s, canonical tags.
- Submit sitemap.xml; monitor coverage in Search Console.
Structured data (schema)
- Add relevant types: Organization, LocalBusiness, Product, Article, FAQ, Breadcrumb.
- Validate with Rich Results Test; avoid spammy or misleading markup.
Content quality (EEAT)
- Demonstrate expertise with real examples, data, and transparent methods.
- Include author bios, last‑updated dates, and editorial guidelines.
- Reference credible sources on a resources page when needed.
UX and accessibility
- Clear navigation, readable fonts, high contrast, ample spacing.
- Keyboard navigable, focus states, descriptive link text.
Off‑page and authority
- Build trust with testimonials, case studies, press mentions, directories.
- Earn links through useful resources, partnerships, and community contributions.
Costs and budget: what to expect
| Site type | Setup cost (est.) | Monthly/ongoing |
| Personal blog / portfolio | $100–$500 | $5–$25 |
| Small business site (5–10 pages) | $500–$5,000 | $20–$100 |
| E‑commerce (10–100 SKUs) | $1,500–$20,000+ | $30–$300 |
| Informational portal/ LMS/ community | Highly variable | Plan for custom features and moderation |
Notes
- Costs vary by scope, custom design/dev, content creation, and integrations.
- Budget time for copywriting, photography, and ongoing content marketing.
Website maintenance checklist
Monthly
- Update CMS, plugins/apps, themes; review security logs.
- Verify backups and run a test restore.
- Fix broken links and 404s; review CWV and performance.
Quarterly
- Content refresh for top pages; add internal links and new CTAs.
- Access review and user cleanup; audit privacy and cookie consent.
- Technical audit: schema, redirects, sitemaps, indexation.
Annually
- Renew domains/certificates; reassess hosting plan and CDN.
- Update brand assets and design system as needed.
Common mistakes to avoid
- No clear goal or CTA on key pages.
- Slow hosting, heavy images, and ignoring mobile UX.
- Plugin/app overload; skipping backups and staging.
- Thin, duplicate, or keyword‑stuffed content.
- No analytics, conversion tracking, or testing.
- Neglecting accessibility and privacy compliance.
Recommended tools and platforms
Domains/DNS and security
- Namecheap, Google Domains (where available), Cloudflare DNS + SSL.
Hosting/CDN
- Managed WordPress (Kinsta, WP Engine), VPS (DigitalOcean/Linode), Shopify for commerce, Cloudflare CDN.
CMS and builders
- WordPress (+ lightweight builder), Shopify, Webflow, Squarespace/Wix (quick start).
Design and content
- Figma/Canva, Unsplash/Pexels, Squoosh/TinyPNG, Hemingway/Grammarly.
SEO and analytics
- Google Search Console, GA4, Screaming Frog, schema generators, Yoast/Rank Math/SEOPress.
Performance and monitoring
- Cloudflare, caching plugins, UptimeRobot/Better Uptime, LogRocket/Hotjar (behavior insights).
Summary
- Websites remain essential for credibility, discovery, and conversions.
- Choose the right type (blog, portfolio, e‑commerce, corporate, portal, LMS, community, membership, nonprofit, landing page).
- Get the fundamentals right: domain, hosting, CMS, clean design, strong content, and ongoing maintenance.
- Follow simple SEO best practices and iterate based on analytics to grow sustainably.
FAQs
What type of website should a small business start with?
- A simple service site: Home, Services, About, Case Studies, Blog, Contact. Focus on local SEO, fast load times, and clear CTAs.
Which platform is best: WordPress, Shopify, or Webflow?
- WordPress: most flexible and cost‑effective for content‑heavy sites. Shopify: best for e‑commerce. Webflow: great for custom design without code.
How much does a website cost per month?
- Expect $20–$100 for hosting, CDN, backups, and a few paid tools/apps. E‑commerce and high‑traffic sites cost more.
How long does it take to build a website?
- A streamlined 5–10 page site can launch in 3–6 weeks. E‑commerce or custom builds may take 8–16+ weeks.
What are the most important SEO steps for a new site?
- Nail search intent, optimize titles/metas and headings, improve speed and mobile UX, add internal links, submit sitemap, and keep publishing quality content.
